Have you ever worried about your private data being exposed on public Wi-Fi? Or wondered how businesses protect sensitive information across the internet? Welcome to the world of VPNs. Understanding what is a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is no longer just a techie issue—today, it’s essential knowledge for online security, cybersecurity professionals, IT managers, and business leaders. This guide will break down how VPNs work, why they matter, and how you can make the most of them.
Understanding the Basics – What is a VPN?
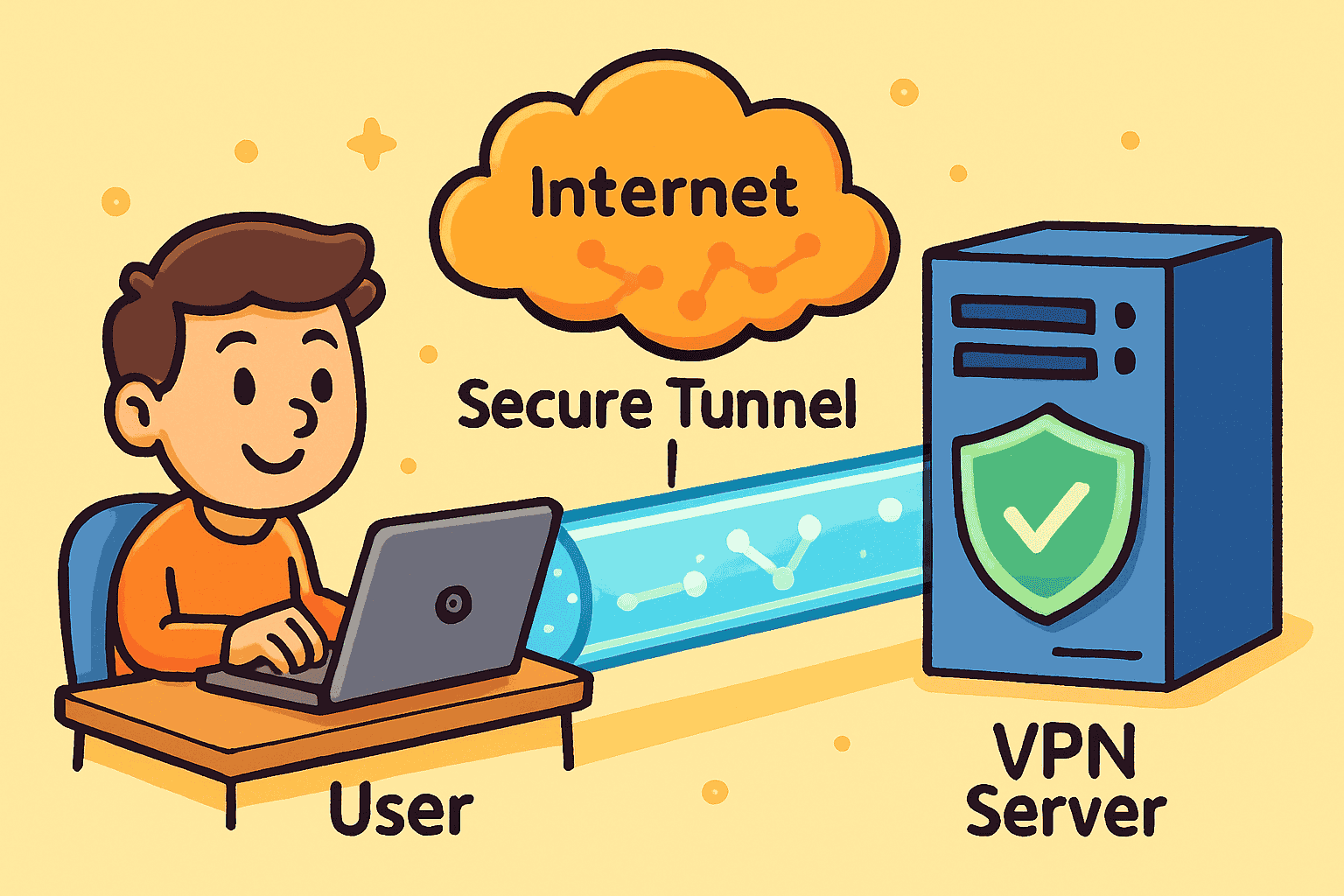
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the wider internet. Think of it as a private tunnel that shields your data from prying eyes, no matter where you connect. By masking your IP address and routing your online activity through a secure server, VPNs give you enhanced privacy and online protection. Whether you manage personal accounts or company data, VPNs play a vital role in keeping information safe in today’s digital world.
How Does a VPN Work?
So, how does a VPN work? Here’s a simple breakdown:
- When you connect to a VPN, your internet traffic first goes to a VPN server.
- The VPN server encrypts your data, creating a secure “tunnel” between your device and its destination online.
- Websites and services see the VPN server’s IP address—not yours.
- As a result, your location and personal data remain private, and your connection is far more secure.
(see the generated image above)
This encrypted tunnel is a crucial part of what makes VPNs effective for both individuals and large organizations.
Key Benefits of Using a VPN
A VPN offers more than just privacy. Here’s what a VPN can do for you:
- Online security and anonymity: Masks your IP for private browsing.
- Protection on public Wi-Fi: Shields your data on shared networks, like airports and cafes.
- Access to restricted content: Lets you bypass geo-blocks to reach the internet freely.
- Business use cases: Enables remote teams to securely access company networks.
In industries where data matters—think healthcare, finance, or tech—a VPN helps meet compliance and privacy requirements while boosting user trust.
Types of VPNs and Protocols
Not all VPNs are built the same. Here are the most common types and protocols:
Types:
- Remote Access VPNs: Securely connect a device to a company network.
- Site-to-Site VPNs: Link two separate networks (like branch offices).
- Mobile VPNs: Support connections over mobile devices and unstable networks.
Common VPN Protocols:
- OpenVPN: Widely used for reliability and security.
- L2TP/IPsec: Known for strong encryption.
- WireGuard: Modern, fast, and lightweight.
- PPTP: Older but often supported by legacy systems.
Understanding these options can help IT managers and CEOs make smart choices about implementation.
Choosing the Best VPN – What to Look For?
With so many options, picking the best VPN can be tricky. Prioritize these features for a better experience:
- Strong security protocols (OpenVPN, WireGuard)
- No-log policy (provider does not store your activity)
- Fast connection speeds
- Multiple device support
- Transparent pricing
- Positive user reviews
For business environments, look for solutions that include centralized management and 24/7 customer support.
Common VPN Myths Debunked
Many misconceptions surround VPNs. It’s time to set the record straight:
- VPNs are only for hackers: In reality, millions use VPNs daily for basic privacy.
- Using a VPN is illegal: VPN usage is legal in most countries—always check local laws.
- VPNs always slow down your internet: Premium VPNs typically have minimal speed impact.
- All VPNs guarantee anonymity: A VPN protects your connection, but true anonymity depends on broader precautions.
Real-World VPN Use Cases by Industry
- Finance: Banks use VPNs to secure online transactions and protect client data.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics rely on VPNs to adhere to data privacy laws and safeguard patient information.
- Education: Schools use VPNs to allow faculty and students to access resources securely from remote locations.
- Technology: Tech companies depend on VPNs for safe remote work and protecting proprietary code.
- Each sector benefits from the data security and flexibility that VPNs provide.
FAQs About VPNs
- What is a VPN used for?
A VPN is used to enhance online privacy, protect personal or business data, securely access remote networks, and bypass content restrictions. - Is VPN safe to use?
When you choose a reputable provider, VPNs are very safe—they encrypt your data and mask your IP address for better protection. - Do I need a VPN?
If you value privacy, regularly use public Wi-Fi, or manage sensitive information, a VPN is a smart choice. - Can a VPN be hacked?
While no technology is 100% hack-proof, top-tier VPNs use advanced encryption and security protocols, making them highly secure. - How do I set up a VPN?
Most VPNs offer easy-to-use apps for all devices—just download, sign up, and connect with one click.
Conclusion & Actionable Tips
A VPN is an essential tool for anyone looking to protect their privacy, secure business data, or simply browse freely. By understanding what is a VPN and how it works, organizations and individuals alike can take charge of their online lives.
Stay proactive—enhance your online security with a trusted VPN today.
For further reading, check out articles on cybersecurity essentials and explore recent VPN industry statistics to stay up-to-date.













Leave a Reply
View Comments